DRY CHEMICAL POWDER FIRE EXTINGUISHING SYSTEMS


The cost incurred to shut down a production line due to a fire can exceed the cost of the actual fire damage. With dry chemical fire suppression systems, fires in process equipment can be rapidly detected, extinguished and production resumed. The sudden extinguishing effect of the powder cloud is caused by the suffocation effect and the anticatalytic effect, a chemical intervention into the combustion process. Extinguishing powders mainly consist of non-poisonous inorganic salts mixed with waterproofing and pouring agents. Dry Chemical powder is an extremely effective fire fighting agent that suppresses fire by inhabiting the chain reaction of combustion and coating the surface of the burning material. The coating separates the fuel from the oxygen supply, and prevents re-flash. The system has the choice of two dry chemical agents effective on Class A, B and C fires. Total flooding or local application design options. The system includes detectors, a control unit, agent storage cylinders, piping and discharge nozzles. Depending on the nature of the equipment under protection, dry chemical systems can be activated manually or automatically using fusible links or heat and smoke detectors.


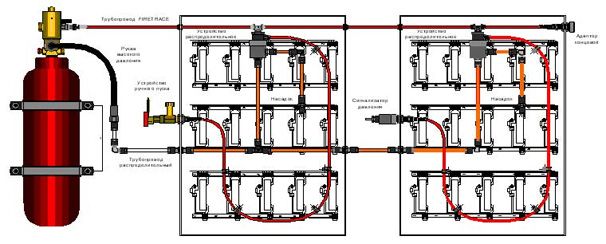
Large powder extinguishing systems
If several rooms and objects are to be protected with powder extinguishing systems, a central powder storage in compression-proof steel vessels, which is sufficient for all protection areas, should be provided.
Small powder extinguishing systems
Small powder extinguishing systems are recommended for objects with a limited scope of protection. To a great extent the design and dimensioning of such powder extinguishing systems is standardized for several similar objects and thus, costs are minimized. They are preferably used in extractor hoods, exhaust air ducts, laboratories and experimenting institutes etc.

Benefits
- Easy to design
- Safe and reliable fire protection
- Flexible installation parameters
Range of application
- Compressor and pump stations
- Utilities substations for oil and gas
- Gas burner stations at boiler plants
- LNG, LPG and chemical tankers
- Quench tanks and coating equipment
- Flammable liquid storage areas
- Hydraulic systems
- Aircraft hangars
- Hazardous waste systems
- Chemical Works
- Oil cellars
- Petrol dumps
- Exhaust ducts



